What is malaria?
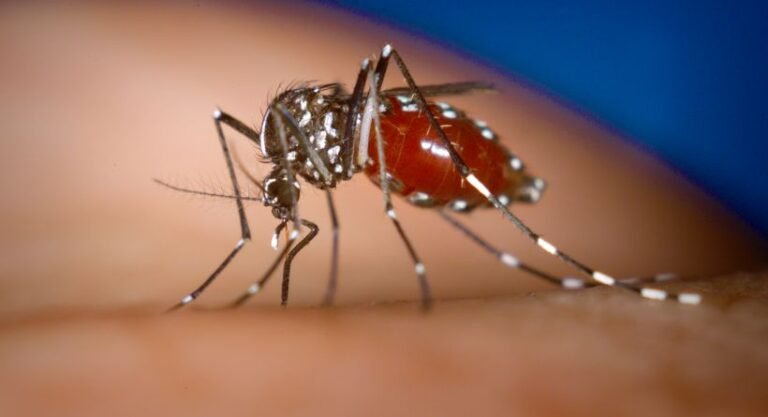
Malaria is a very dangerous illness carried by the bite of a mosquito carrying microscopic parasites. Malaria parasites are injected into the bloodstream by a mosquito bite. Parasites, not viruses or certain bacteria, are responsible for malaria.
Without treatment, malaria may lead to convulsions, brain damage, difficulty breathing, organ failure, and death.
In the United States, only approximately 2,000 instances of the illness are reported annually. Please with your healthcare practitioner before going to a region where malaria is prevalent. The illness may be transferred from sick travellers to the United States if they are bitten by a mosquito, which would then bite another person.
Also read: d2l mnsu.edu
How common is malaria?
Tropical regions with high temperatures and high humidity tend to have higher rates of malaria. There were 241 million cases of malaria recorded worldwide in 2020, with 627,000 fatalities attributed to the disease. The continents of Africa and South Asia account for the lion’s share of these occurrences.
Where does malaria usually occur?
Though it is more common in tropical regions and places with high humidity, malaria may strike anywhere:
- Africa.
- Latin America and Central America.
- The Caribbean region, including the Dominican Republic, Haiti, and elsewhere.
- Europe to the East.
- Parts of South and Southeast Asia.
- Oceanic islands located in the middle and lower reaches of the Pacific (Oceania).
Who might get malaria?
Malaria may affect everyone, but those who reside in Africa are more vulnerable. The risk of death from malaria is higher for the young, the elderly, and pregnant women. Complications from the condition are more common in low-income people who lack access to medical treatment.
Young children make up virtually all of the over 90% of malaria victims in Africa. In 2020, younger children (those less than five) accounted for more over 80% of malaria fatalities in the area.
What causes malaria?
Malaria is spread when mosquitoes feed on infected humans. Parasites are transmitted from one human to another by mosquito bites. Parasites thrive in that environment. There are five different parasites that cause malaria in humans.
Malaria may be passed from a pregnant mother to her unborn child under very unusual circumstances.
Malaria might theoretically be transmitted by blood transfusions, organ donations, and hypodermic needles, although this is quite improbable.
What are the symptoms of malaria?
Signs and symptoms of malaria may include:
- Fever
- Chills
- General feeling of discomfort
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Muscle or joint pain
- Fatigue
- Rapid breathing
- Rapid heart rate
- Cough
Some persons with malaria suffer from recurrent episodes of illness. Chills and fever are frequently the first symptoms of an attack, followed by perspiration and a return to normal temperature.
Within a few weeks of being bitten by a mosquito carrying malaria, the first symptoms often appear. Yet, certain malaria parasites may remain latent for up to a year in the human body.
Diagnosis
In order to diagnose malaria, your doctor would most likely look at your medical history, inquire about your recent travel plans, do a physical exam, and request blood tests. A blood test may reveal…
- It is necessary to have the parasite present in your blood to diagnose malaria.
- Can you identify the kind of malaria parasite that is causing your illness?
- If the parasite causing your illness is drug-resistant, you may not be able to get well for a long time.
- Do any severe consequences from the condition exist?
Depending on the test, bloodwork might take anywhere from 15 minutes to several days. Your doctor will decide what extra diagnostic tests to do based on your symptoms.
Also read: reddit uk musictamburrogamerevolution
Treatment
Medicines that target the malaria parasite are used to treat the disease. The medicine selection and duration of therapy will be conditional on the following factors:
- Which type of malaria parasite you have
- The severity of your symptoms
- Your age
- Whether you’re pregnant
Is there a vaccine against malaria?
In a trial study, researchers in Ghana, Kenya, and Malawi created and tested a vaccination for kids. Plasmodium falciparum is the most common form of malaria in children, and the RTS, S/AS01 vaccination is very effective against this deadly parasite.
What is the outlook for people who have malaria?
Malaria may cause major health issues, including irreversible organ damage and death, if it is not treated effectively. If you have just returned from a region where malaria is prevalent, or if you suspect that you have malaria, you should be checked out as soon as possible. Beginning treatment early has been shown to have a dramatic influence on patient outcomes.
Plagued by malaria? Not if you take the proper drug at the appropriate dosage. You can develop malaria again if you are bit by an infected mosquito, even if you’ve had it previously.