Top Quality Control Tools That Empower Process Improvement and Product Reliability
In a competitive business landscape, delivering high-quality products and services is vital for success. One of the most effective ways to achieve this is by using quality control tools. These tools provide structured techniques to identify, analyze, and resolve process-related issues, ensuring consistency and continuous improvement.
What Are Quality Control Tools?
Quality control tools are proven methods used to monitor, evaluate, and enhance operational performance. They help teams detect defects, reduce variation, and maintain process stability. These tools are applicable across industries—whether in manufacturing, service, healthcare, or IT.
Businesses use Quality Control Tools to gain insights into workflows, find root causes of problems, and take corrective actions. By making data-driven decisions, organizations can avoid costly errors and deliver reliable outcomes.
Why Are Quality Control Tools Essential?
Implementing Quality Control Tools improves product quality, reduces waste, and boosts customer satisfaction. These tools help teams visualize processes and data, making it easier to understand where and why problems occur. This enables more effective solutions and promotes a culture of continuous improvement.
They also support compliance with industry regulations, reduce risk, and ensure long-term operational success.
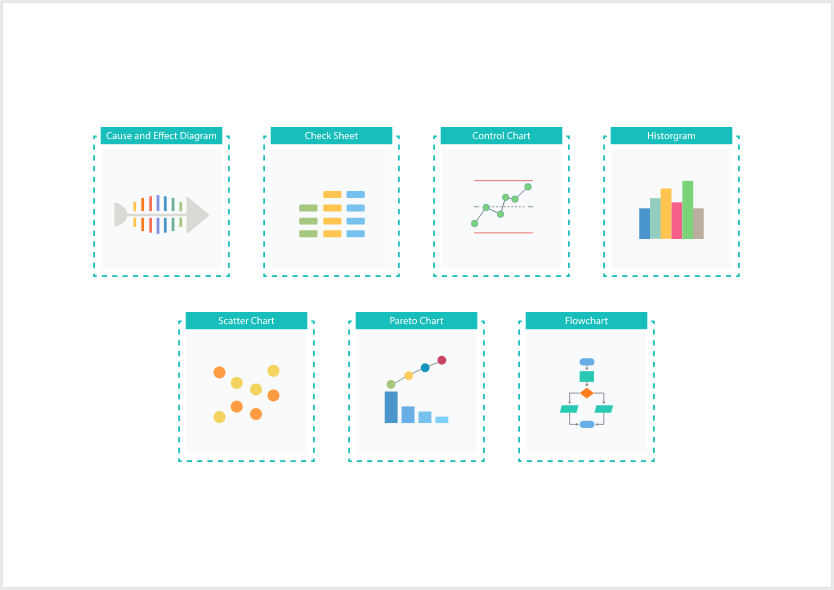
The 7 Foundational Quality Control Tools
These seven classic tools are essential for any business striving for high-quality results:
- Cause-and-Effect Diagram (Fishbone/Ishikawa)
Breaks down potential causes of a problem into categories, helping pinpoint root issues. - Check Sheet
A structured method for collecting data on defects, errors, or incidents in real time. - Control Chart
Tracks process behavior over time to determine if it remains within acceptable limits. - Histogram
Shows data distribution and helps identify patterns or variations in a process. - Pareto Chart
Prioritizes issues by frequency or impact, highlighting the most critical problems. - Scatter Diagram
Explores the relationship between two variables to detect possible correlations. - Flow Chart
Visualizes process steps, making it easier to find inefficiencies, delays, or bottlenecks.
How to Make the Most of Quality Control Tools
- Define the issue you want to improve
- Select the most appropriate tool based on the nature of the problem
- Gather accurate, relevant data for analysis
- Collaborate with cross-functional teams for broader insight
- Implement changes and monitor outcomes over time
Conclusion
Quality control tools are powerful assets for businesses aiming to deliver excellence and foster continuous growth. They bring structure, clarity, and precision to problem-solving efforts, leading to better products, satisfied customers, and efficient processes. When consistently applied, these tools lay the foundation for sustainable success and a strong reputation for quality.