Sleep Apnoea Treatment in Singapore: Options for Better Sleep and Health
Sleep apnoea is a common yet serious sleep disorder that affects breathing during sleep, often leading to frequent interruptions in rest. This condition can result in daytime fatigue, poor concentration, and long-term health complications such as high blood pressure and heart disease. Identifying and addressing sleep apnoea is essential for overall well-being and quality of life.
If you are experiencing symptoms like loud snoring, choking or gasping during sleep, and excessive daytime drowsiness, seeking sleep apnoea treatment in Singapore can help manage the condition and improve your sleep quality. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can assist in making informed decisions about your health.
What Is Sleep Apnoea?
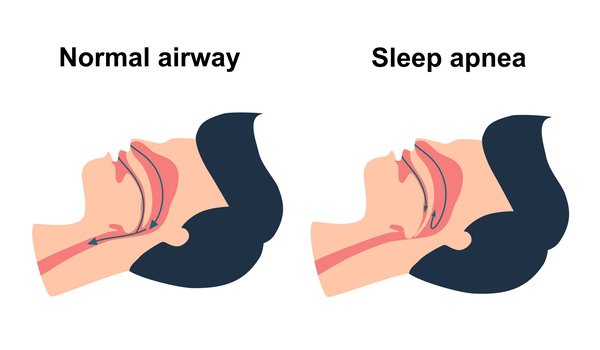
Sleep apnoea occurs when breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep due to blocked airways or poor brain signal transmission. These interruptions reduce oxygen levels in the body, affecting overall health and increasing the risk of cardiovascular problems.
There are three main types of sleep apnoea:
1. Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA)
This is the most common form and occurs when throat muscles relax excessively, blocking airflow. Risk factors include obesity, nasal congestion, smoking, and a family history of the condition.
2. Central Sleep Apnoea (CSA)
This less common type results from the brain failing to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. CSA is often linked to medical conditions such as heart failure or neurological disorders.
3. Complex Sleep Apnoea Syndrome
Also known as treatment-emergent central sleep apnoea, this occurs when a person has both obstructive and central sleep apnoea.
Symptoms of Sleep Apnoea
Recognizing the symptoms of sleep apnoea can help in early diagnosis and treatment. Common signs include:
- Loud and persistent snoring
- Episodes of choking or gasping during sleep
- Frequent nighttime awakenings
- Morning headaches
- Dry mouth or sore throat upon waking
- Daytime sleepiness and fatigue
- Difficulty concentrating
- Mood changes such as irritability or depression
If you experience these symptoms regularly, consulting a healthcare professional can help determine the severity of the condition and the best course of action.
Sleep Apnoea Treatment Options in Singapore
Various treatment options are available in Singapore to manage sleep apnoea and improve overall sleep health. The right treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying causes.
1. Lifestyle Modifications
For mild cases of sleep apnoea, making lifestyle changes can help reduce symptoms. These include:
- Weight Management: Excess weight, particularly around the neck, can put pressure on the airway. Losing weight may help reduce airway obstruction.
- Sleeping Position Adjustment: Sleeping on your side rather than your back can prevent airway collapse.
- Avoiding Alcohol and Sedatives: These substances relax throat muscles and can worsen sleep apnoea.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking increases inflammation in the airways, making breathing more difficult.
2. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Therapy
CPAP therapy is one of the most effective treatments for moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnoea. A CPAP machine delivers a steady flow of air through a mask to keep the airway open during sleep. Benefits of CPAP therapy include:
- Reduction in snoring and breathing interruptions
- Improved oxygen levels during sleep
- Better overall sleep quality and daytime alertness
3. Oral Appliance Therapy
For individuals who cannot tolerate CPAP, oral appliances may be an alternative. These custom-fitted devices reposition the jaw and tongue to keep the airway open. Benefits include:
- Comfort and ease of use compared to CPAP
- Portability for travel
- Effectiveness in mild to moderate cases
4. Surgical Options
Surgery may be recommended in severe cases where other treatments are ineffective. Surgical options include:
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP): Removal of excess throat tissue to widen the airway.
- Genioglossus Advancement (GA): Repositioning of tongue muscles to prevent airway blockage.
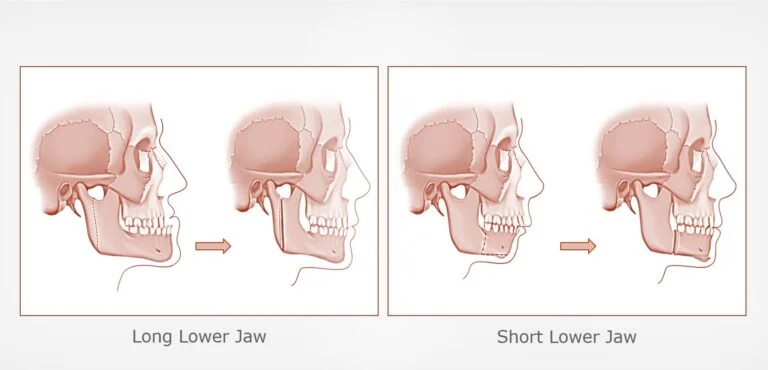
- Maxillomandibular Advancement (MMA): Realignment of the upper and lower jaw to create more space in the airway.
5. Positional Therapy
Some individuals experience worsened sleep apnoea when sleeping on their back. Positional therapy involves using special pillows or devices to encourage side sleeping, reducing airway obstruction.
6. Oxygen Therapy
For individuals with central sleep apnoea or those who experience low oxygen levels during sleep, supplemental oxygen therapy may be prescribed to ensure proper oxygenation.
7. Myofunctional Therapy
This therapy involves exercises that strengthen the tongue and throat muscles to prevent airway collapse. It can be particularly beneficial for individuals with mild to moderate sleep apnoea.
Risks of Untreated Sleep Apnoea
Ignoring sleep apnoea can lead to serious health complications, including:
- High blood pressure
- Heart disease and stroke
- Type 2 diabetes
- Increased risk of accidents due to daytime sleepiness
- Poor mental health, including anxiety and depression
Seeking timely treatment can help prevent these risks and improve overall well-being.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you suspect you have sleep apnoea, consulting a healthcare provider is essential. A sleep study (polysomnography) may be conducted to assess breathing patterns, oxygen levels, and sleep quality. Based on the results, a tailored treatment plan can be recommended.
Conclusion
Sleep apnoea is a serious condition that can significantly impact sleep quality and overall health. Fortunately, a variety of treatment options are available in Singapore, ranging from lifestyle modifications and CPAP therapy to oral appliances and surgical procedures. Addressing sleep apnoea early can improve breathing, enhance sleep quality, and reduce the risk of long-term health complications. If you experience symptoms, seeking professional evaluation and treatment can help restore restful sleep and overall well-being.